The chemical basis for life
Objectives:
1. Identify the chemical bases of life
2. Understand how the chemical bases for life support life on earth
3. Understand how properties of water, organic molecules, and enzymes work together to create living things
Essential Questions:
What are the chemical bases of life and how are they important?
How do living things use the chemical bases of life to stay alive?
Key Terms:
Lipids - organic compounds they are fatty acids. They are made up of natural oils, waxes, and steroids.
Cohesion - when similar molecules stick together.
Adhesion - when dissimilar molecules stick together.
Freezing point - when a liquid transforms into a solid at a center cool temperature (32℉).
Organic compounds - compounds that contain carbon.
Macromolecules - a molecule that contains a lot of atoms like nucleic acids, and proteins.
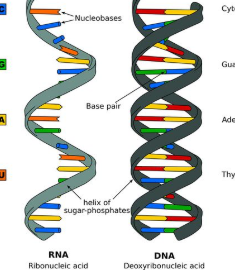
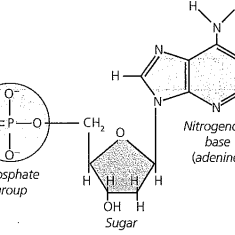
Nucleic Acids - organic substances in living cells like DNA and RNA which are made up of lots of nucleotides
Proteins - nitrogenous organic compounds that have large molecules made up of long chains of amino acids.
Enzymes - a substance created by an organism that is a stimulus for biochemical reactions.
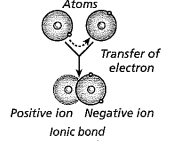
The chemical bases for life are necessary for the survival of living organisms. Living organisms could not survive on earth without water. Most of an organism cells are made up of water. The average human body is up to 65% water. Most reactions that happen in a cell include substances that are dissolved in water. A water molecule has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (h2O) held together by covalent bonds. Bonds form between atoms that share electrons. Atoms in a covalent bond don't always share an equal amount of electrons this is called a polar covalent bond. An ionic compound is made up of two ions with different charges. Water is a molecule that is polar so, it can dissolve other polar molecules. Water is known as a universal solvent because it can dissolve polar and ionic substances. Although there are some substances that don’t dissolve easily in water lipids are made up of nonpolar molecules so they are insoluble in water. Lipids are a type of macromolecule. Cohesion is when similar molecules stick together and Adhesion is when dissimilar molecules stick together. An example of adhesion is water staying on the tip of a pine needle after its rained. Water has the ability to absorb and retain heat this is known as specific heat. Water has a substantial density as a liquid than a solid. The freezing point is when a liquid becomes a solid the freezing point of water is 32℉. Lipids are fats, oils, waxes, and sterols. Lipids are made .up of mostly carbon and hydrogen atoms. Other types of macromolecules and nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleotides adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine, and uracil make DNA and RNA strands hydrogen bonds hole these strands together. DNA and RNA carry genetic information. Proteins are also macromolecules that perform some of the cell's functions. Proteins are made up of amino acids which contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Some proteins are enzymes that carry out chemical reactions without them it would be hard to survive.
Multiple Choice and Open-Ended Questions:
1. Most of an organism's cells are made up of water
A. True
B. False
2. At what temperature does liquid freeze?
A. 13℉
B. 4℉
C. 27℉
D. 32℉
3. Water staying on the tip of a pine needle after it rained is an example of which of the following?
A. cohesion
B. adhesion
C. photosynthesis
D. hydrolysis
4. Explain the differences between cohesion and adhesion
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
5. Explain what happens during a chemical reaction
_______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________